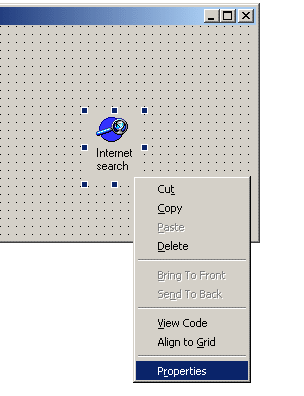
Include SearchEngine ActiveX control in your Visual Basic Form and using right button of your mouse invoke 'Properties' as shown on snapshot below
Internet Search ActiveX 1.0
Overview
Please visit www.lencom.com for the latest updates
Content
Recomended strategy
Steps to define new search engine
SearchEngines ActiveX
control
Methods
StartSearch
StopAll
ShowSelectEngines
Clear
ApplicationIdExists
LoadEnginesByApplicationID
SaveListByAPPID
Properties and collections
ApplicationID
AllResults
ActiveEngines
busy
UpdateURL
UpdateDays
Events
OnSearchDone
OnPageDone
OnProgress
SearchResult Object
SearchEngine Object
SearchEngines collection
SearchEnginesObject Object
Recomended strategy
There are 2 ways to ask
ISA to do something for You. First one is to invoke some method that returns
results synchronically as soon as it's done or second that takes the parameters of
your search and performs search in background, just raising OnSearchDone event when
its done to let You use the results. First way
is good for ASP pages or any processes that run in background
anyway and second is for usual user interface programming. For first case is
recommended to use SearchEnginesObject and for second is SearchEngines control.
Steps to define new search Engine
Step 1.
Include SearchEngine ActiveX control in your Visual Basic
Form and using right button of your mouse invoke 'Properties' as shown on
snapshot below

Step 2
Click 'Define engine' button on properties tab. 'Search engine
properties' dialog will appear.
Step 3
Fill up appropriate fields using 'Search engine properties' dialog
.
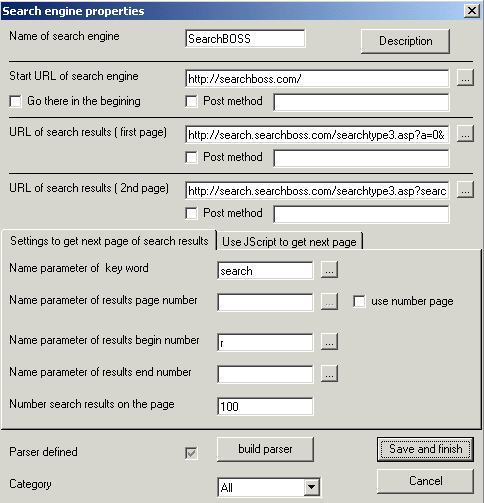
| FIELD | DESCRIPTION |
| Name of search engine | Any search engine that You define suppose to have short and understandable name. Because this name will be used as a key to find the engine , it's strongly recommended not to use spaces or special characters. For example 'MyEngine' is a good name but 'My Engine' or 'My-Engine' are not. |
| Start URL |
The start URL is used for opening working
session with target web site ,if required, before doing any search. The
good example of such need is login action. For example if You have
username and password for employment web site , You should login ,provide
that URL for this field and mark 'Go there in the beginning's checkbox. If
You don't need open the session , anyway it's good idea to provide some
URL that leads to main page. For example for 'Yahoo' should
be defined 'http://www.yahoo.com' Please use button ... to navigate there and select it without typing. |
| URL of search results (first page) | The URL address of the first page of search
results can be different from the second and other pages. Please use
button ... to navigate there. Please use button ... to navigate there and select it without typing. |
| URL of second page | Please use button ... to navigate there and select it without typing. |
| Maximum results | A lot of search engines are showing off telling You on search results page something like 'Results 1 - 10 of about 32,000,000. ' They don't tell You that if You need all of 32000000 You CAN'T have it. After 10th or 20th page the engine will refuse to continue. You should investigate your engine and provide a maximum number of search results available. |
| Name parameter of key word | http://www.onesearch.com/cb/os.cgi?q=car&id=&s=11&p=2&a=10&slu=2411237481008722359 The URL above brings search results from 'onesearch' using 'car' as the search word. Which variable in that URL is equal to 'car'? Of course q . Please use ... button to do it without typing. |
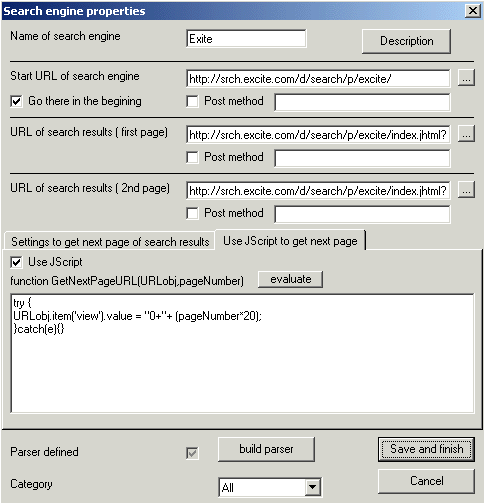
| Name parameter of page number | http://search.microsoft.com/us/dev/default.asp?qu=webbrowser&ig=06&p=2 http://www.onesearch.com/cb/os.cgi?q=car&id=&s=11&p=2&a=10What's the structural difference between 2 URLS above? First URL uses page numbers to list results (parameter p) while second one uses number of result to start from , to display second result page. If your search engine uses pages You should specify parameter name and mark 'use number page' checkbox. |
| Name parameter of begin number | http://search.microsoft.com/us/dev/default.asp?qu=webbrowser&ig=06&p=2 http://www.onesearch.com/cb/os.cgi?q=car&id=&s=11&p=2&a=10 What's the structural difference between 2 URLS above? First URL uses page numbers to list results (parameter p) while second one uses number of result to start from , to display second result page. If your search engine uses number of result to start from , You should specify name of the parameter. (in our example it's 'start' for second URL) |
| Name parameter of end number | http://search.aol.com/dirsearch.adp?query=car&first=11&last=25 Please take a look how well known provider defines its second page of search results. It declares not only number result to start from but number result to finish the display. If your engine has it please provide it here. |
| Number results per page | Any page of search results has a number results on the page. Just count them and enter the number here. |
| Parser definition | To have a data instead of HTML page our ActiveX control needs a parser. The description of how to define the parser is below this table. |
| Category | It's easier to browse engines when they're categorised. If the category does not exist yet please select 'All' . You can define category and edit the engine later. |
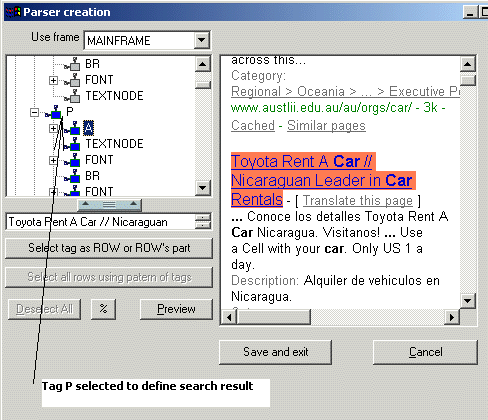
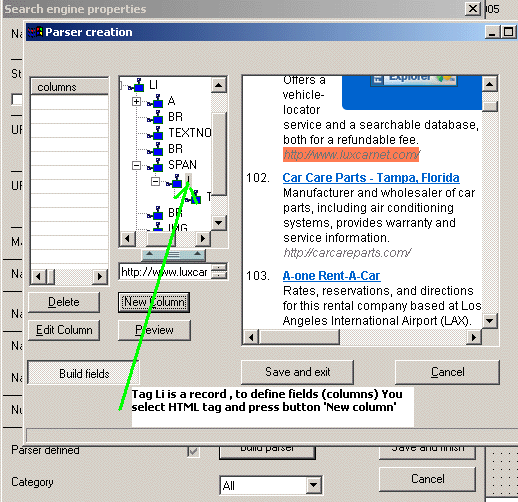
Sometimes search results have a complicated structure . Just to have text or URL is not enough. The columns (or fields) are designed to parse the records itself extracting required parts from the search result.
On your component tab an icon of the control will appear as show
After You added the control to the form, next required step is to select engines that will be involved in the search. At design time You can do it using custom interface of the control or at the run time You can add it using AddEngine method in ActiveEngines collection , for example SearchEnginesCTRL1.ActiveEngines.AddEngine "Yahoo" adds Yahoo.com to the list . Now your project is ready to use the control.
StartSearch method
Syntax
res = object.StartSearch(searchWords, NumerResultsPerPage)Parameters
searchWords Optional. String that specifies one or several key words for the search query. By default will be used words that specified within definition of search engine NumerResultsPerPage Optional. Number that defines how many records .
Return Value
Returns True if a search started , false otherwise
Remarks
This method starts Internet search that will be completed by raising OnSearchDone event.
Syntax
object.StopAll(RaiseOnSearchDoneEvent)Parameters
RaiseOnSearchDoneEvent Optional. Boolean that tells the control to raise or not OnSearchDone event. By default is True.
Return Value
Doesn't return any value
Remarks
This method stops any search operations and release all object involved in the search. The boolean parameter should be False if the method called when windows application is being destroying , otherwise
True is recommended.
Syntax
object.ShowSelectEngines(readOnly)Parameters
readOnly Optional. Boolean that tells the control that User can't edit search engines definitions. By default is False.
Return Value
Doesn't return any value
Remarks
This method shows User Interface window that provides ability to Add/Remove engines for the current search.
Syntax
object.ClearReturn Value
Doesn't return any value
Remarks
The method clears search results and sets AllResults.Count property to 0
Syntax
object.ApplicationIDExists(AppID)Parameters
AppID Required. String that uniquely identifies your application on local computer.
Return Value
Boolean, True if application ID exists on local computer , False otherwise.
LoadEnginesByApplicationID method
Syntax
object.LoadEnginesByApplicationID (AppID)Parameters
AppID Required. String that uniquely identifies your application on local computer.
Return Value
Doesn't return any value
Remarks
This method loads list of selected engines from the disk. The List can be saved using SaveListByAPPID method. If the application ID does not exist the exception will be thrown.
Syntax
object.SaveListByAPPID(AppID)Parameters
AppID Required. String that uniquely identifies your application on local computer.
Return Value
Doesn't return any value
Remarks
This method saves list of selected engines to the disk. The List can be loaded using LoadEnginesByApplicationID method
Syntax
object .ApplicationIDReturn Value
Sets and returns string that identify windows application on local computer. Can be used to save/load list of engines across different applications.
Syntax
res = object .busyReturn Value
Read only . Returns True if a search in progress, false otherwise
Remarks
Use this property to verify the status of the control
Syntax
object.UpdateURLReturn Value
Sets and returns string that specify URL for the update procedure.
Remarks
UpdateDays and UpdateURL properties define source(URL) and frequency for build-in automatic update process of the control. Every UpdateDays days process will start , download update file from UpdateURL , add new engines if any , update engines with the identical names , but will never delete any engine on local computer.
Syntax
object.UpdateDaysReturn Value
Sets and returns number days between starting an update procedure. If -1 the update never starts.
Remarks
UpdateDays and UpdateURL properties define source(URL) and frequency for build-in automatic update process of the control. Every UpdateDays days process will start , download update file from UpdateURL , add new engines if any , update engines with the identical names , but will never delete any engine on local computer.
Syntax
object.ActiveEngineReturn Value
Sets and returns reference to collection of SearchEnegine objects.
Remarks
The collection is 1 based and indexed by engine's name. It has the same methods and properties as any VB collection - item , count , add. This is an VB example how to access to SearchEngine object
set myObj=SearchEnginesCTRL1.ActiveEngines.item("Yahoo")
Syntax
object.AllResultsReturn Value
Sets and returns reference to collection of SearchResult objects.
Remarks
The collection is 1 based and not indexed. It has the same methods and properties as any VB collection - item , count , add. This is an VB example how to access to SearchResult object
set myObj=SearchEnginesCTRL1.AllResults.item(1)
Syntax
object_OnSearchDone()Remarks
Occurs when all search engines completed their work. The property busy switches to False and the results of the search available via AllResults collection.
Syntax
object_OnPageDone(ByVal NewResults As Object, ByVal pDisp As Object, ByVal URL As String, ByVal EngineName As String)Parameters
NewResults Collection of SearchResult objects that extracted from the one page of the search results. pDisp Object that specifies the top-level or frame WebBrowser object corresponding to the event. For more information please check out MSDN documentation. URL String that specifies the URL, Universal Naming Convention (UNC) file name, or pointer to an item identifier list (PIDL) of the loaded document. EngineName String that specifies the name of search engine.
Remarks
This event occurs when new page of the search results has been downloaded and parsed. Instead of waiting till all the engines will complete their work, user can use the results of the fastest search engine.
dim sRes as SearchResult
dim ii as Long
for ii=1 to NewResults.count
set sRes = NewResults.item(ii)
List1.AddItem sRes.URLS(1) 'adds to listbox first URL of search result
List1.AddItem sRes.FullText 'adds to listbox text of search result
List.AddItem " " 'adds space to listbox for better view
next
Syntax
object_OnProgress(ByVal status As String)Parameters
status String that describes status of currently working search engine.
Remarks
The event occurs when status of any working search engines is changed.
This object hosts the information about one search
result. The following members are available
Fields collection
Syntax
object.Fields.item(byval index as variant)Return Value
Sets and returns reference to collection of strings where each of them is a column(field) extracted from the search result. All columns(fields) should be predefined with parser creation procedure. The collection has standard methods Add , Item,Remove,Count
Remarks
This is an VB example how use the collection. The example supposes that field 'Price' was defined when the parser was created.
dim sRes as SearchResult
for each sRes in SearchEnginesCTRL1.AllResults
List1.AddItem sRes.Fields("Price") 'adds price to the listBox
List1.AddItem sRes.Fields(3) ' the same by number
Next
FullText property
Syntax
object.FullTextReturn Value
Sets and returns string that contains full text of the search result
Remarks
This is an VB example how use the property
dim sRes as SearchResult
for each sRes in SearchEnginesCTRL1.AllResults
List1.AddItem sRes.FullText 'adds text to the listBox
Next
URLS collection
Syntax
object.URLSReturn Value
Sets and returns reference to collection of strings where each of them is URL extracted from the search result. The collection has standard methods Add , Item,Remove,Count
Remarks
The collection is 1 based and not indexed. This is an VB example how use the collection
dim sRes as SearchResult
dim URL as string
dim ii as Long
for each sRes in SearchEnginesCTRL1.AllResults
for ii= 1 to sRes.URLS.Count
URL = sRes.URLS.Item(ii) 'now variable URL has a value.
Next
Next
HTMLObjects collection
Syntax
object.HTMLObjectsReturn Value
Sets and returns reference to collection of HTML elements where each of them is HTML object extracted from the search result. This collection is available only when OnPageDone event occurs and after this event will be cleared. The references to HTML objects shouldn't be stored in client application. The collection has standard methods Add , Item,Remove,Count
Remarks
This object hosts the technical information about search engine. The following members are availableThe collection is 1 based and not indexed. For more information about properties and methods of HTML object please look at Microsoft documentation. This is an VB example how use the collection
dim sRes as SearchResult
dim htmlObj as Object
dim htmlCollection as Object
dim ii as Long
dim i as Long
for each sRes in NewResults
for ii= 1 to sRes.HTMLObjects.Count
Set htmlObj = sRes.HTMLObjects.Item(ii) < BR> Set htmlCollection = htmlObj.all.tags("A") 'extracts all "A" tags if any
for i=0 to htmlCollection.length 'html collection is 0 based
List1.AddItem htmlCollection(i).hostname
Next
Next
Next
Name property
Syntax
object.NameEngineReturn Value
Sets and returns string that contains name of the engine
Remarks
This is an VB example how use the property
dim Eng as SearchEngine
for each Eng in SearchEnginesCTRL1.ActiveEngines
List1.AddItem Eng.NameEngine 'adds name to the listBox
Next
OptionsURL property
Syntax
object.OptionsURLReturn Value
Sets and returns string that contains options URL of the engine. The address used for the search engines that require log in before search operations
StartURL property
Syntax
object.StartURLReturn Value
Sets and returns string that contains address of the first page results of the engine. The address's used for the search engines that have different format to retrieve first and all next pages.
SecondpageURL property
Syntax
object.SecondPageURLReturn Value
This collection holds SearchEngine object and besides standard Add,Remove,Item,Count methods has the following memberSets and returns string that contains address of the second page results of the engine. The address's used for the search engines that have different format to retrieve first and all next pages
Syntax
Set Eng = object.AddEngine(NameEngine)Parameters
NameEngine String that identifies engine. The definition of the engine should be pre created , otherwise exception will occur.
Return Value
Returns reference to the new SearchEngine Object
Example
SearchEnginesCTRL1.ActiveEngines.AddEngine "Yahoo"
SearchEnginesCTRL1.StartSearch "xml", 50
This object provides all required methods to
perform search synchronously. The intended use of the object is ASP pages and
other background processes. The object exposes 2 methods
AddEngine method
Syntax
Set Eng = object.AddEngine(NameEngine)Parameters
NameEngine String that identifies engine. The definition of the engine should be pre created , otherwise exception will occur.
StartSearch method
Syntax
Set sRes = object.StartSearch(searchWords, NumerResultsPerPage,NumberResultsThatEnough) Parameters
searchWords Optional. String that specifies one or several key words for the search query. By default will be used words that specified within definition of search engine NumerResultsPerPage Optional. Number that defines how many records suppose to be returned by every search engine . NumberResultsThatEnough Optional. Number that defines how many records is enough for this search .
Return Value
Returns reference to collection of SearchResult objects
Remarks
This method
starts Internet search
and waits till all the searches will be completed or number results is
more then specified maximum. ASP example
<% Dim r,s,sr
set s =
Server.CreateObject("LNSearchEngines.SearchEnginesObject")
s.AddEngine
"Yahoo"
Set r =
s.StartSearch("xml", 250, 50) 'pay attention , the search will be
for each sr in
r
'done when 50
results retreived
Response.Write "URL = " &
sr.URLS(1) & "<BR>" & sr.FullText &
"<BR><BR>"
Next
Set s = Nothing
Set r = Nothing
Set sr =
Nothing
%>< BR >